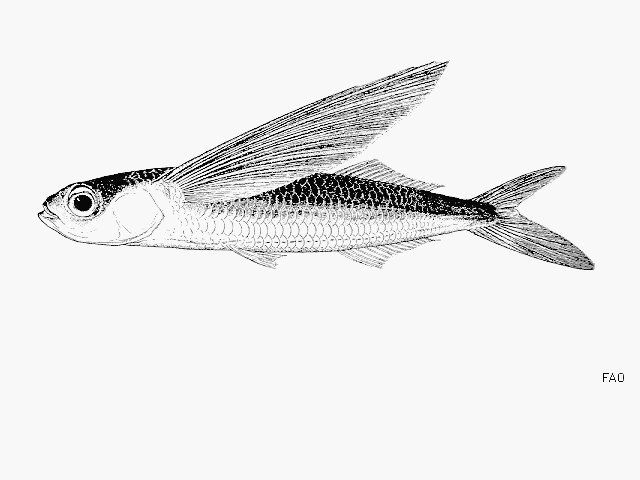
| Exocoetidae (Flyingfishes) |
| 30 cm TL (male/unsexed) |
|
pelagic-neritic; marine; depth range 0 - 20 m, oceanodromous |
| Widespread in tropical and subtropical zones of all oceans including the western Mediterranean Sea and part of the Caribbean Sea (Ref. 3720), probably absent in the inland seas of southeastern Asia (Sulawesi Sea, Sulu Sea, Flores, Banda, Ceram and Halmahera seas (Ref. 27313)), and the Benguela Current (Ref. 4498). Eastern Pacific: Mexico to central Chile; also the Galapagos and Hawaii. Western Pacific: Japan, Marshall Islands, Philippines, Australia (Ref. 5530), and Tahiti. |
|
Dorsal spines (total): 0-0; Dorsal soft rays (total): 12-15; Anal spines: 0-0; Anal soft rays: 12-14; Vertebrae: 43-46. Body dark, iridescent blue above, silvery white below; pectorals and caudal fin greyish, other fins not pigmented (Ref. 2797). Juveniles with or without black bars (Ref. 2797). Branchiostegal rays: 9-11 (Ref. 36606). |
| Adults occur in surface waters, both near and far from the coast (Ref. 5217). Form schools. Capable of leaping out of the water and gliding for long distances above the surface. Feed mostly on crustaceans and other planktonic animals. Preyed upon by swordfish, tunas and many other larger pelagic fishes (Ref. 9987). Oviparous, with planktonic eggs and larvae (Ref. 36606). |
|
Least Concern (LC); Date assessed: 28 January 2013 Ref. (130435)
|
| harmless |
Source and more info: www.fishbase.org. For personal, classroom, and other internal use only. Not for publication.