Teleostei (teleosts) >
Clupeiformes (Herrings) >
Engraulidae (Anchovies) > Coiliinae
Etymology: Thryssa: Greek, thrissa, -es = shad (Ref. 45335).
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Marine; brackish; pelagic-neritic; depth range 1 - 20 m (Ref. 6898). Tropical; 28°N - 40°S, 21°E - 170°E (Ref. 189)
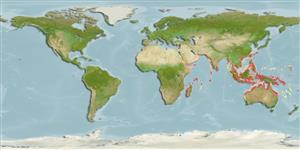
Indo-Pacific: India Ocean from Gulf of Oman south to Port Alfred, but no records from the Red Sea and Madagascar; coasts of Pakistan, India and probably Burma; Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines to Taiwan (Ref. 189), including Arafura Sea (Ref. 9819); also northern Australia, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands and New Hebrides (Ref. 189).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 16.0 range ? - ? cm
Max length : 18.0 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9822); common length : 15.0 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9822)
Dorsal spines (total): 0; Dorsal soft rays (total): 14 - 16; Anal spines: 0; Anal soft rays: 32 - 39. Diagnosis: Body fairly compressed, belly with 16-18 plus 9-10, with a total of 25-28 keeled scutes; lower gill rakers 10-12; head with gold tints; anal and caudal fins deep yellow; a black area behind upper part of gill opening (Ref. 189). It is distinguished from all other Thryssa species and in fact all other anchovies by the very long maxilla, reaching at least to tip of pectoral fin, usually to pelvic fin base or even to anal fin origin; also unique is the high coronoid process of the lower jaw, the jaw rising steeply in the mouth (Ref. 189).
Marine, pelagic, presumably schooling, occurring mostly close inshore, entering bays and estuaries (Ref. 189, 30573). Recorded at a temperature range of 26.0-29.0 °C in the Trinity Inlet system, Australia (Ref. 4959). It feeds mainly on crustaceans, like amphipods, zoea larvae, Acetes (Ref. 189, 30573). May be caught using ringnets (Ref. 5213). Used as bait in the tuna fishery in the South Pacific.
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Wongratana, T., T.A. Munroe and M. Nizinski, 1999. Order Clupeiformes. Engraulidae. Anchovies. p. 1698-1753. In K.E. Carpenter and V.H. Niem (eds.) FAO species identification guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of the WCP. Vol. 3. Batoid fishes, chimaeras and bony fishes part 1 (Elopidae to Linophrynidae). FAO, Rome. (Ref. 9822)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; bait: usually
Tools
Can't connect to MySQL database fbquizv2. Errorcode: Too many connections