Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
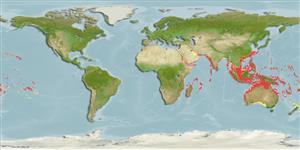
Marine; brackish; reef-associated; depth range 1 - 200 m (Ref. 89972), usually ? - 50 m (Ref. 37816). Tropical; 29°N - 39°S, 24°E - 122°W (Ref. 5222)
Indo-Pacific: Red Sea to Algoa Bay, South Africa and eastward to the Hawaiian and Pitcairn islands, north to southern Japan, south to Australia. Absence in the Persian Gulf is puzzling.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ?, range 129 - ? cm
Max length : 270 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5213); common length : 190 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5450); max. published weight: 400.0 kg (Ref. 26367)
Dorsal spines (total): 11; Dorsal soft rays (total): 14 - 16; Anal spines: 3; Anal soft rays: 8. This species is distinguished by the following characters: robust body, its width 1.5-1.75 in body depth; body depth 2.3-3.4 in SL (for specimens 12-179 cm SL); head length 2.2-2.7 in SL; eye diameter 5.8-14 in HL; interorbital width 3.3 (at 177 cm SL) to 6.2 (at 12 cm SL) in HL; preopercle finely serrate, the corner rounded; upper edge of operculum convex; midlateral part of lower jaw with 2-3 rows of teeth (at 20-25 cm SL) increasing to 15-16 rows in specimen of 177 cm SL; canine teeth at front of jaws small or absent; pill rakers of first gill arch 8-10 + 14-17; dorsal fin third to eleventh spines subequal, shorter than longest soft rays; short pelvic fins, 23.0-2.7 in head length; caudal fin rounded; lateral-line scales 54-62, the anterior scales with branched tubules (except small juveniles). Colour: small juveniles (less than 15 cm) yellow, with 3 irregular black areas, the first from spinous dorsal fin to belly and chest and extending onto head, the second from base of soft dorsal fin to anal fin and the last at base of caudal fin; subadults (25-60 cm) with irregular white or yellow spots on the black areas and fins with black spots; adults (90-165 cm) dark brown with faint mottling, the fins with numerous small black spots; large adults 180-250 cm) dark brown, fins darker (Ref. 39231, 89707, 90102).
The largest bony fish found in coral reefs (Ref. 9710). Individuals more than a meter long have been caught from shore and in harbors. Common in shallow waters. Found in caves or wrecks; also in estuaries. Juveniles secretive in reefs and rarely seen (Ref. 48635). Benthopelagic and benthic (Ref. 58302). Feed on spiny lobsters, fishes, including small sharks and batoids, and juvenile sea turtles and crustaceans. In South African estuaries, the main prey item is the mud crab, Scylla serrata. Unconfirmed reports of fatal attacks on humans. Nearly wiped out in heavily fished areas (Ref. 9710). Large individuals may be ciguatoxic (Ref. 37816). In the Hong Kong live fish markets (Ref. 27253). It is not common enough to be of commercial importance; rare in some places due to spearfishing; also caught with hook-and-line and spear (Ref. 39231).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Heemstra, P.C. and J.E. Randall, 1993. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 16. Groupers of the world (family Serranidae, subfamily Epinephelinae). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of the grouper, rockcod, hind, coral grouper and lyretail species known to date. Rome: FAO. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(16):382 p. (Ref. 5222)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Threat to humans
Traumatogenic (Ref. 4690)
Human uses
Fisheries: subsistence fisheries; aquaculture: commercial; gamefish: yes; aquarium: commercial
Tools
Can't connect to MySQL database fbquizv2. Errorcode: Too many connections