Teleostei (teleosts) >
Eupercaria/misc (Various families in series Eupercaria) >
Labridae (Wrasses) > Cheilininae
Etymology: Cheilinus: Greek, cheilos = lip (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Bloch.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
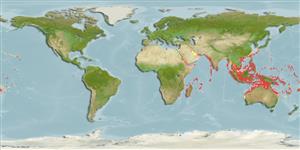
Marine; reef-associated; depth range 4 - 80 m (Ref. 9823), usually 4 - 40 m (Ref. 27115). Tropical; 23°C - 27°C (Ref. 27115); 32°N - 36°S, 24°E - 170°W
Indo-Pacific: from the east coast of Africa and islands of the western Indian Ocean to Micronesia and Samoa and Tonga; north to the Ryukyu Islands, Japan; south to Queensland, Australia.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 40.0 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9823); max. published weight: 172.83 g (Ref. 124708)
Dorsal spines (total): 9; Dorsal soft rays (total): 10; Anal spines: 3; Anal soft rays: 8. This species is distinguished by the following characters: body moderately deep, its depth 2.35 to 2.6 times in standard length; dorsal profile of head convex; anterior tip of snout forming an acute angle; jaws prominent, especially lower jaw in large individuals; strong canines 2, situated anteriorly in each jaw; no enlarged tooth present on rear of upper jaw; D IX,10, continuous with spines and anterior soft rays of similar length; A III, 8; pectoral fins with ii unbranched and 10 branched rays; pelvic fins short, not reaching anus; caudal fin rounded in juveniles, the upper and lower rays forming elongate lobes in large individuals, giving the fin a trilobed appearance. Lateral line interrupted below posterior portion of dorsal-fin base, with a total of 22-23 pored scales; scales reaching well onto bases of dorsal and anal fins; scales in front of dorsal fin extending forward to above anterior portion of eye; cheek and opercle scaly; lower jaw without scales (Ref. 9823). Colour of juveniles brown with 5 white bars across body, the first broadest and brightest, below third dorsal-fin spine, the second bar indistinct, on ventral half of body and the fifth is faint, anteriorly on caudal peduncle; all bars but the second extend onto dorsal and anal fins; 3 faint, short, greenish bars on nape and interorbital space; short, oblique, white or yellowish band from eye across preopercle; narrow white bar at base of caudal fin; large, dark blue spot, surrounded dorsally with orange, anteriorly in dorsal fin. Colour of subadults and females with similar white bars on nape and body as juveniles, but the second bar on lower body becoming more distinct and nearly reaching dorsal fin; there are few scales behind eyes and many scales on body with vertical indistinct dark streak; an orange area from behind eye and nape to pectoral-fin base; humeral area with 2 (sometimes a third above) double, rounded to nearly quadrangular, dark blue or black spots; head becoming olive with short orange-red lines radiating from eye; the lower body, dorsal and anal fins, and posterior half of caudal fin with small dark orange to red spots, only a few spots in fins in some individuals, sometimes median fins also with short red lines, similar to those radiating from eye; caudal fin is white with black bar in centre (bar not reaching upper and lower margins) and black posterior margin. Colour of males with similar color pattern but the suffusion of orange becoming bright orange-red, covering postorbital part of head, anterior of body (including anterior abdomen and chest), and pectoral-fin base, the area restricted posteriorly to the first white bar, not enclosing it; a second white bar across the body reaching dorsal fin; black streak on scales becoming broader and well-defined (Ref. 117607).
Adults inhabit lagoon and seaward reefs, usually in areas with mixed coral, sand, and rubble (Ref. 9710). Young common on silty reefs, usually along edges with algae-rubble and sand (Ref. 48636). Juveniles are secretive. Individuals often solitary and mainly on sand and rubble substrata near coral reefs, but more common in protected than exposed areas, generally at depths less than 20 m. (Ref. 117607). Feed mainly on benthic, hard-shelled invertebrates, including mollusks, crustaceans and sea urchins (Ref. 5374). Oviparous, distinct pairing during breeding (Ref. 205). Caught on hook-and-line with some frequency, this species is marketed in small numbers. Occasionally seen in the aquarium trade (Ref. 9823). Maximum depth reported taken from Ref. 128797.
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Oviparous, distinct pairing during breeding (Ref. 205).
Bogorodsky, S.V., T.J. Alpermann and A.O. Mal, 2016. Redescription of Cheilinus quinquecinctus Rüppell, 1835 (Pisces: Perciformes, Labridae), a valid endemic Red Sea wrasse. Zootaxa 4158(4):451-472. (Ref. 117607)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; aquarium: commercial
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 24.7 - 29, mean 28 °C (based on 1620 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5078 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01585 (0.00700 - 0.03587), b=2.95 (2.76 - 3.14), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this (Sub)family-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.4 ±0.40 se; based on food items.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (Preliminary K or Fecundity.).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Moderate vulnerability (39 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 38.5 [21.3, 85.9] mg/100g; Iron = 0.618 [0.276, 1.406] mg/100g; Protein = 17.6 [13.4, 21.0] %; Omega3 = 0.103 [0.059, 0.172] g/100g; Selenium = 35.3 [17.8, 77.5] μg/100g; VitaminA = 217 [41, 973] μg/100g; Zinc = 2.82 [1.59, 4.57] mg/100g (wet weight); based on
nutrient studies.