Teleostei (teleosts) >
Syngnathiformes (Pipefishes and seahorses) >
Centriscidae (Snipefishes and shrimpfishes) > Centriscinae
Etymology: Centriscus: Derived from Greek, kentris, -idos = sting (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Linnaeus.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
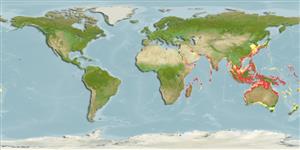
Marine; brackish; reef-associated; depth range 2 - 100 m (Ref. 37816), usually 2 - 15 m (Ref. 90102). Tropical; 34°N - 35°S, 32°E - 172°E
Indo-Pacific: Red Sea and Arabian Gulf (Ref. 11441) to New Guinea, north to southern Japan, south to New South Wales, Australia.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 17.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 110387)
Inhabits sandy or muddy floors of shallow inlet waters. Usually in large schools among branching corals, seawhip gardens and black coral bushes to about 15 m depth. Small juveniles in surface waters and sometimes in small groups along beach edges in quiet bays and settle with crinoids or urchins (Ref. 48635). Usually processed into fishmeal (Ref. 2858).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Masuda, H., K. Amaoka, C. Araga, T. Uyeno and T. Yoshino, 1984. The fishes of the Japanese Archipelago. Vol. 1. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, Japan. 437 p. (text). (Ref. 559)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquarium: commercial
Tools
Can't connect to MySQL database fbquizv2. Errorcode: Too many connections