Teleostei (teleosts) >
Gobiiformes (Gobies) >
Gobiidae (Gobies) > Gobiinae
Etymology: Rhinogobiops: Greek, rhinos = nose + Latin, gobius = gudgeon Greek, ops = similar to; nicholsii: Named after Capt. H.E. Nichols, U.S.N, its discoverer (Ref. 6885).
Eponymy: Captain Henry Ezra Nichols (d: 1899) was a US Navy officer at the Department of Alaska. [...] (Ref. 128868), visit book page.
More on author: Bean.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
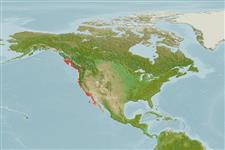
Marine; demersal; depth range 0 - 106 m (Ref. 2850). Subtropical; 55°N - 27°N, 136°W - 114°W
Eastern Pacific: Wales Island, northern British Columbia, Canada to Punta Rompiente, central Baja California, Mexico.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 15.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 2850); max. reported age: 5 years (Ref. 56049)
Found usually in sandy areas near rocks. Occurs from intertidal areas to 106 m depth. Retreats to rocks or holes when approached. Young are found usually offshore among plankton. Oviparous (Ref. 56079). A protogynous hermaphrodite (Ref. 34256). Forms permanent harem groups composed of a single male and several smaller females (Ref. 55367). Eggs are guarded by the male (Ref. 56079).
Nesting occurs from April-October. Male cleans spawning site under rock, then attracts female by rising from bottom to display his black pelvic disk. Male guards nest after female lays eggs. Protogynous (Ref. 13452, 35501). Sex reversal is completed in less than 5 months (Ref. 34185, 34256). A monandric species (Ref. 55367). Length at sex change = 6.9 cm TL (Ref. 55367). Also Ref. 103751.
Eschmeyer, W.N., E.S. Herald and H. Hammann, 1983. A field guide to Pacific coast fishes of North America. Boston (MA, USA): Houghton Mifflin Company. xii+336 p. (Ref. 2850)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquarium: public aquariums
Tools
Can't connect to MySQL database fbquizv2. Errorcode: Too many connections