Mola
mola
(Linnaeus,
1758)
Ocean sunfish
View all media / Upload your photos and videos
Expand all
Classification / Names
Teleostei (teleosts) > Tetraodontiformes (Puffers and filefishes) >
Molidae (Molas or Ocean Sunfishes)
Etymology: Mola: Latin, mola, -ae = stone mill; because of the shape of this fish (Ref. 45335).
More on author:
Linnaeus.
Environment / milieu / depth range / climate zone / distribution range
Distribution
Circumglobal: tropical and temperate zones of all oceans.
Maps
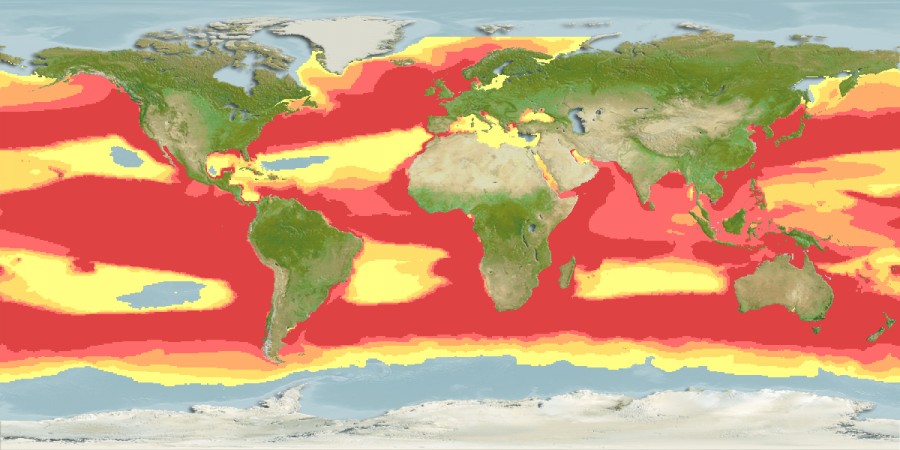
Mola mola / Native range
AquaMaps Data sources:
GBIF
OBIS
This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed.

Mola mola / Suitable habitat
AquaMaps Data sources:
GBIF
OBIS
This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed.

Mola mola / Point map
AquaMaps Data sources:
GBIF
OBIS
This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed.

Mola mola / Year 2050
AquaMaps Data sources:
GBIF
OBIS
This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed.
Size / Weight / Age
Short description
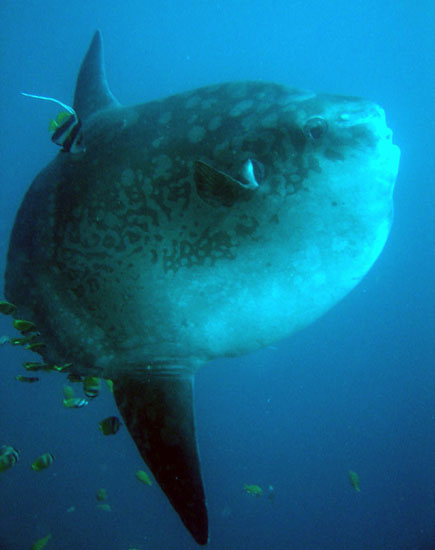
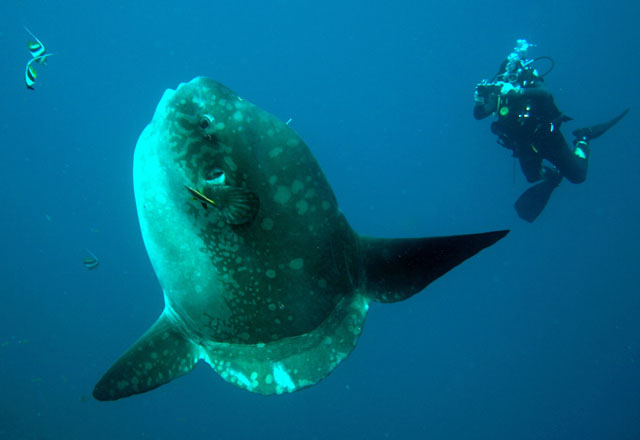
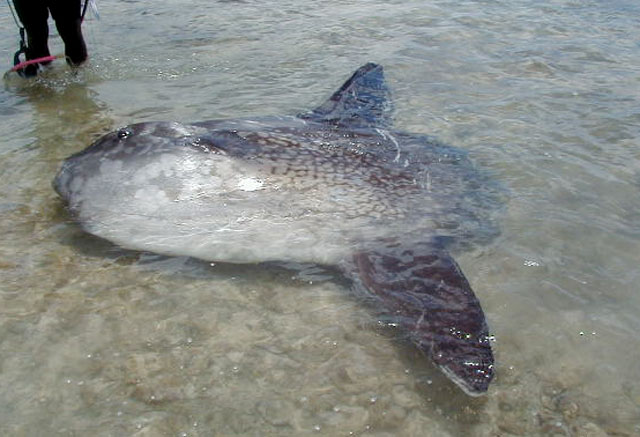
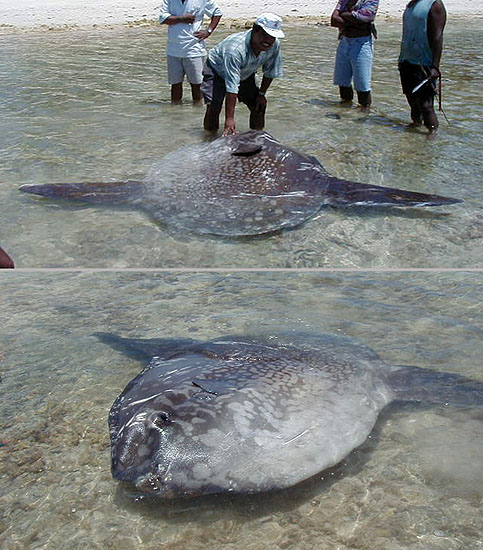
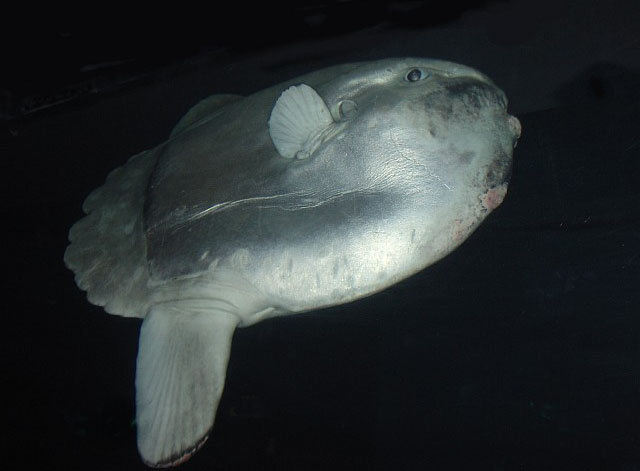
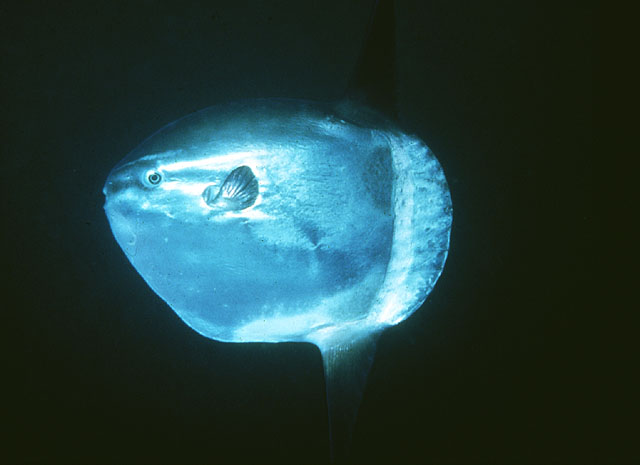
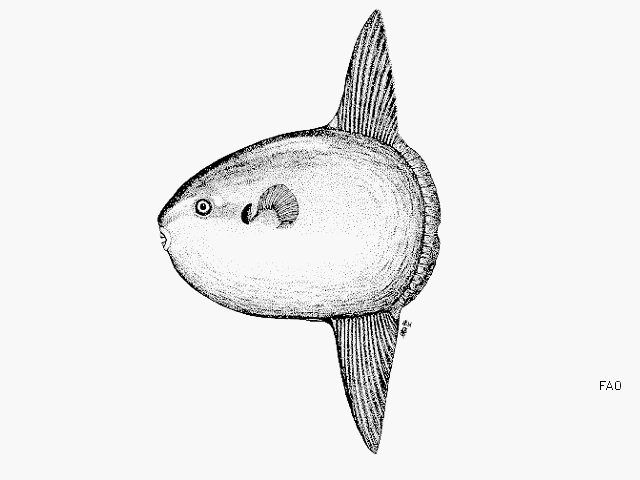
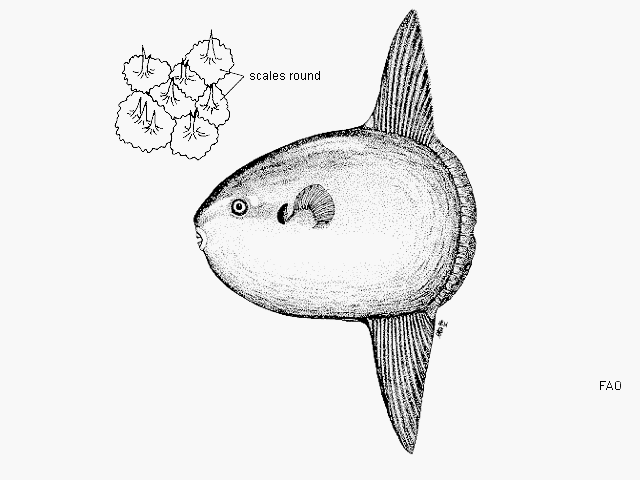
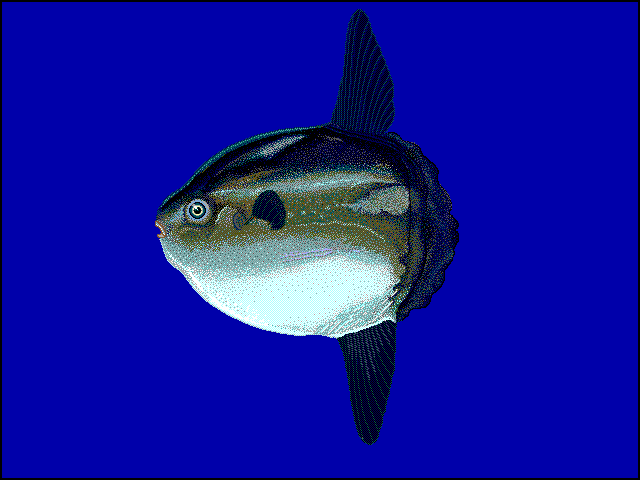
Dorsal spines (total): 0; Dorsal soft rays (total): 15 - 18; Anal spines: 0; Anal soft rays: 14 - 17. The scaleless body is covered with extremely thick, elastic skin. The caudal fin is replaced by a rudder-like structure called 'clavus'. Dorsal and anal fins very high with short base; in swimming, these fins are flapped synchronously from side to side and can propel the fish at surprisingly good speed. Pectorals small and rounded, directed upward (Ref. 6885). Mouth very small; teeth fused to form a parrot-like beak. Gills 4, a slit behind the last; gill openings reduced to a small hole at the base of the pectoral fins. Gas bladder absent in adults. Description: Characterized further by deep and oval body, nearly circular, depth 1-1.5 in TL; rough texture of skin; clavus supported by about 12 fin rays, of which 8-9 bear ossicles (Ref. 90102).
Biology
Molas are distinguished for their distinct morphological characters which include reduced/fused caudal elements, presence of a clavus in place of the caudal fin, absence of a swim bladder and a degenerate, cartilaginous skeleton (Ref. 86435). Adults are found on slopes adjacent to deep water where they come in for shelter and for seeking cleaner fishes. They are usually shy. However, they may become familiar with divers in some locations (Ref. 48637). Individuals often drift at the surface while lying on its side but can swim actively and are capable of directional movements otherwise (Ref. 86435). They swim upright and close to the surface. The dorsal fin often protrudes above the water. Females are larger than males (Ref. 86435). This species has been filmed in 480 m depth with the help of a camera equipped with baits (Lis Maclaren, pers. comm. 2005). Adults eat fishes, mollusks, zooplankton, jellyfish, crustaceans and brittle stars (Ref. 4925, 5951, 48637). A live colony of the cirripede Lepas anatifera were found attached to the anterior portion of the sunfish's esophagus that was stranded in the south coast of Terceira Island, Azores Archipelago in 2004. This association has apparent advantages for the goose barnacles such as a regular intake of food and protection both from hydrodynamic hazards and from predators: but for the sunfish, it is not clear whether it is neutral, of advantage or causes feeding problems since the attachment may obstruct the sunfish's esophagus (Ref. 55063). The sunfish is registered as the heaviest bony fish and as the one with the most eggs in the Guinness Book of World Records (Ref. 6472). Generally this species is not used as food fish; some people consider it as a delicacy (Ref. 30573). The fish can be utilized fresh and can be broiled (Ref. 9988). Some parts of the fish are used in Chinese medicine (Ref. 12166). Molas may contain the same toxin as puffers and porcupine fish (Ref. 13513). They do not adapt well in captivity (Ref. 12382, 37040). Juveniles are victims of California sea lions in Monterey Bay (Ref. 37040).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Main reference
Tortonese, E. 1990 Molidae. p. 1077-1079. In J.C. Quero, J.C. Hureau, C. Karrer, A. Post and L. Saldanha (eds.) Check-list of the fishes of the eastern tropical Atlantic (CLOFETA). JNICT, Lisbon; SEI, Paris; and UNESCO, Paris. Vol. 2. (Ref. 6952)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 125652)
Vulnerable (VU), A4bd; date assessed: June 07 2011
CITES (Ref. 131153)
Not Evaluated
CMS (Ref. 116361)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Poisonous to eat (Ref. 13513)
More information
- Countries
- FAO areas
- Ecosystems
- Occurrences
- Introductions
- Stocks
- Ecology
- Diet
- Food items
- Food consumption
- Ration
- Common names
- Synonyms
- Metabolism
- Predators
- Ecotoxicology
- Reproduction
- Maturity
- Spawning
- Spawning aggregation
- Fecundity
- Eggs
- Egg development
- Age/Size
- Growth
- Length-weight
- Length-length
- Length-frequencies
- Morphometrics
- Morphology
- Larvae
- Larval dynamics
- Recruitment
- Abundance
- References
- Aquaculture
- Aquaculture profile
- Strains
- Genetics
- Allele frequencies
- Heritability
- Diseases
- Processing
- Mass conversion
- Vision
- Pictures
- Stamps, Coins Misc.
- Sounds
- Ciguatera
- Speed
- Swim. type
- Gill area
- Otoliths
- Brains
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref. 123201): 5.3 - 20.5, mean 10.2 °C (based on 1286 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref. 82804): PD50 = 0.6562 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.02455 (0.01023 - 0.05892), b=3.01 (2.80 - 3.22), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this (Sub)family-body shape (Ref. 93245).
Trophic level (Ref. 69278): 3.1 ±0.4 se; Based on food items.
Generation time: 7.4 ( na - na) years. Estimated as median ln(3)/K based on 1 growth studies.
Resilience (Ref. 120179): Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (tmax assumed > 15; Fec=300 million (batch fecundity)).
Fishing vulnerability (Ref. 59153): High to very high vulnerability (67 of 100).
Climate vulnerability (Ref. 125649): Moderate vulnerability (43 of 100).
Price category (Ref. 80766): Unknown.
Nutrients (Ref. 124155): Calcium = 19.4 [7.7, 46.5] mg/100g; Iron = 0.967 [0.481, 2.428] mg/100g; Protein = 18.7 [16.3, 21.0] %; Omega3 = 0.248 [0.113, 0.569] g/100g; Selenium = 57.6 [22.6, 165.5] μg/100g; VitaminA = 3.53 [0.76, 16.47] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.381 [0.234, 0.617] mg/100g (wet weight);