Teleostei >
Clupeiformes (Herrings) >
Alosidae (Shads and Sardines)
Etymology: Alosa: Latin, alausa = a fish cited by Ausonius and Latin, halec = pickle, dealing with the Greek word hals = salt; it is also the old Saxon name for shad = "alli" ; 1591 (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Linnaeus.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
生态学
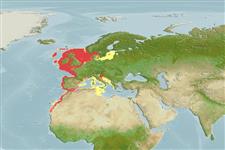
海洋; 淡水; 半咸淡水; 溯河洄游 (Ref. 89642); 深度上下限 10 - 300 m (Ref. 10536). 溫帶; 61°N - 20°N, 17°W - 22°E
Eastern Atlantic: from southern Norway and along the coasts of Europe to northern Mauritania (Ref. 188, 6683), including the Western Baltic Sea up to the Kaliningrad Oblast (Ref. 12801, 26334, 59043), the western part of Mediterranean Sea (Ref. 188, 6683, 59043) and the coasts of northern Africa (Ref. 3509). However, presently only very locally distributed outside France, victim of pollution and impoundment of large rivers throughout Europe (Ref. 59043).
東大西洋: 從卑爾根 (挪威) 沿著對在非洲中的茅利塔尼亞北部的歐洲的海岸。 (參考文獻 188, 參考文獻 51442) 也在地中海的西部中.(參考文獻 188) 記錄來自了波羅的海西部海洋向上到加里寧格勒州.(參考文獻 12801,26334) 伯恩公約的附錄 3(受保育的動物群).
Length at first maturity / 大小 / 重量 / 年龄
Maturity: Lm 47.8, range 45 - 50 cm
Max length : 69.0 cm TL 雄鱼/尚未辨别雌雄; (Ref. 10536); 83.0 cm TL (female); common length : 40.0 cm TL 雄鱼/尚未辨别雌雄; (Ref. 2945); common length :70 cm TL (female); 最大体重: 4.0 kg (Ref. 30578); 最大年龄: 10 年 (Ref. 10536)
背棘 (总数) : 0; 背的软条 (总数) : 18 - 21; 臀棘: 0; 臀鳍软条: 20 - 27; 脊椎骨: 57 - 58. Diagnosis: Body somewhat compressed, fairly deep with depth at pectoral fin more than head length, scutes apparent along belly (Ref. 188, 51442). Upper jaw with a distinct median notch, lower jaw fitting into it; no teeth on palatine and vomer; gillrakers long, thin and numerous, a total of 85 to 155 on first arch, longer than gill filaments (Ref. 188, 6683, 59043). A dark spot posterior to gill opening, but sometimes absent, sometimes followed by several small blotches (Ref. 188, 59043). Alosa alosa resembles Alosa fallax, which has fewer and shorter gillrakers and 7 or 8 black spots along flank (Ref. 188).
身体略微扁长形的, 相当深的在胸鳍超过头长随着深度.(参考文献 188, 参考文献 51442) 上颌凹槽, 下颌嵌入它。 (参考文献 188) 鳃耙长的,细的与很多的, 总计 85 到 130, 长度超过鳃丝.(参考文献 188) 大又细的鳞片.(参考文献 51442) 出现腹部的鳞甲。 (参考文献 51442) 一个深色斑点在鳃裂后面 (有时不存在; 偶然地 1 或 2 更多的斑点).(参考文献 188)
Amphihaline species, schooling and strongly migratory, penetrating far up rivers but not into small tributaries (Refs. 188, 59043). Adults are usually found in open waters along the coast (Ref. 51442). In freshwater, inhabits major rivers but may also enter tributaries, if water temperature is equal to or is warmer than the main river (Ref. 188, 10536). Known lake populations from Morocco and Portugal need access to rivers to spawn (Refs. 10536, 89647, 89648). Larvae and small juveniles inhabit deep slow-flowing areas of rivers (Ref. 89649), some swimming upstream in late summer and autumn (Ref. 10536). Juveniles (up to 1+ years) are usually found near estuaries or river mouths (Refs. 10536, 59043), possibly making vertical diurnal movements synchronized with the tides; they remain in estuaries for over one year (Ref. 89630). Feeds on a wide range of planktonic crustaceans; larger adults feed on small schooling fishes (Ref. 188, 51442, 59043). Juveniles in freshwater prey on insect larvae. Females in European rivers commonly reach 70 cm total length (Ref. 10536). Females grow faster and are always larger than males of the same age (Ref. 10536). Less common than Alosa fallax but both have suffered from pollution and weirs or other obstructions (Ref. 188). It has been suggested that members of the genus Alosa are hearing specialists with the American shad (Alosa sapidissima) having been found to detect and respond to sounds up to at least 180 kHz (Ref. 89631). This may aid in predator avoidance (e.g. cetaceans) (Ref. 89632). Hybridization with the twaite shad (Alosa fallax) has been reported from the Rhine (Ref. 89633) as well as from rivers in France and Algeria (Ref. 10536). Shad hybrids may reproduce (Ref. 27567). Marketed fresh and frozen; eaten sautéed, broiled, fried and baked (Ref. 9988).
Amphihaline 种, 在海洋中度过它大部分的生活期.(参考文献 51442) 群游性而强烈的回游性种, 穿透在河川最上游, 但是不进入小的支流之内.(参考文献 188) 五月时进入河中产卵, 通常在晚上与水流是迅急的地方.(参考文献 188) 回游成鱼不进食。 (参考文献 30578) 成鱼在产卵此时稚鱼之后回车大海移动秋天时向下至海洋.(参考文献 188) 吃宽范围的浮游性甲壳动物; 较大的成鱼吃小的群游性鱼。 (参考文献 188, 参考文献 51442) 比 Alosa fallax不普遍但是两者已经蒙受污染与鱼梁或其他的障碍.(参考文献 188) 在市场上销售生鲜和冷冻; 吃煎炒, 火烤了, 油炸了而且烧烤了.(参考文献 9988)
Life cycle and mating behavior
成熟度 | 繁殖 | 产卵场 | 卵 | 孕卵数 | 仔鱼
Adults in the sea begin to move towards the coast in February and congregate near or in estuaries (Ref. 10536). They ascend rivers in April and May when water temperature is 9-12 °C, peaking at 13-16 °C. Adults may migrate up to 700 km from the sea into major rivers and occasionally into the largest tributaries of these rivers to spawn (Ref. 10536). Males migrate upriver at 3-9 years; females first reproduce 1-3 years later than males. Gametogenesis occurs during spawning migration.
Males arrive first in the upper reaches and occupy appropriate spawning sites, with females arriving 1-2 weeks later (Ref. 10536). Spawning sites are usually shallow areas (<1.5 m depth) of rivers near a confluence with strong currents and clean gravel bottoms (Refs. 188, 10536, 59043). Spawning occurs at night (over several nights), in large and very noisy schools that form near the surface.when water temperature reaches at least 15 °C and is believed to be optimal between 22-24 °C. (Ref. 88171). Coupling happens side by side, thrashing caudal fins on water surface and swimming in circles while expulsing eggs and sperms in the surrounding water. Eggs are fertilized in mid-water and then sink to the gravel bottom. Eggs hatch after 4-8 days (22-24 °C) (Ref. 89630). After spawning, adults return to the sea but many die before reaching it (Ref. 188, 51442, 59043). Only 5-6 % of the adults spawn more than once in their lifetime (Ref. 89655). After 3-4 months juveniles (8-12 cm length) move towards the sea until mature (Ref. 10536). Individual fish apparently return to their natal spawning site (Ref. 59043). Also Refs. 5744, 5745.
東大西洋: 從卑爾根 (挪威) 沿著對在非洲中的茅利塔尼亞北部的歐洲的海岸。 (參考文獻 188, 參考文獻 51442) 也在地中海的西部中.(參考文獻 188) 記錄來自了波羅的海西部海洋向上到加里寧格勒州.(參考文獻 12801,26334) 伯恩公約的附錄 3(受保育的動物群).
Whitehead, P.J.P., 1985. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 7. Clupeoid fishes of the world (suborder Clupeoidei). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of the herrings, sardines, pilchards, sprats, shads, anchovies and wolf-herrings. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(7/1):1-303. Rome: FAO. (Ref. 188)
世界自然保护联盟红皮书 (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
人类利用
渔业: 低经济; 游钓鱼种: 是的
工具
特别资料
下载 XML
网络资源
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 7 - 15.6, mean 10.1 °C (based on 480 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00631 (0.00515 - 0.00773), b=3.09 (3.05 - 3.13), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref.
93245).
营养阶层 (Ref.
69278): 3.0 ±0.2 se; based on diet studies.
回复力 (Ref.
120179): 中等的, 族群倍增时间最少 1.4 - 4.4年 (K=0.19-0.29; tm=3.5; tmax=10).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Moderate vulnerability (36 of 100).
Climate Vulnerability (Ref.
125649): Moderate to high vulnerability (47 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 11.2 [4.4, 59.5] mg/100g; Iron = 0.629 [0.269, 1.334] mg/100g; Protein = 19.1 [16.5, 21.8] %; Omega3 = 1.27 [0.69, 2.44] g/100g; Selenium = 15.2 [7.4, 29.9] μg/100g; VitaminA = 15.2 [3.5, 65.1] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.323 [0.203, 0.541] mg/100g (wet weight); based on
nutrient studies.