Teleostei (teleosts) >
Perciformes/Scorpaenoidei (Scorpionfishes) >
Scorpaenidae (Scorpionfishes or rockfishes) > Caracanthinae
Etymology: Caracanthus: Greek, kara = face + Greek, akantha = thorn (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Gray.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
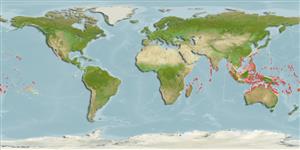
Marine; reef-associated; depth range 1 - 15 m (Ref. 86942). Tropical; 32°N - 24°S
Indo-Pacific: East Africa to the Tuamoto Islands, north to southern Japan and the Ogasawara Islands, south to the Great Barrier Reef.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 5.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 2334)
Facultative air-breathing (Ref. 126274); Found among branches of Stylophora mordax and certain Acropora corals (Ref. 9710). It never ventures outside the confines of the coral head where it swims between the branches foraging for other coral-dwelling types (Ref. 275). Anterolateral glandular groove with venom gland; at least in dorsal-fin spines (Ref. 57406).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Paxton, J.R., D.F. Hoese, G.R. Allen and J.E. Hanley, 1989. Pisces. Petromyzontidae to Carangidae. Zoological Catalogue of Australia, Vol. 7. Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, 665 p. (Ref. 7300)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Human uses
Tools
Can't connect to MySQL database fbquizv2. Errorcode: Too many connections