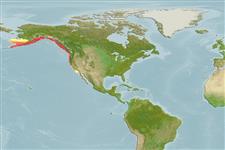
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
marin démersal; oceano-estuarine (Ref. 51243); profondeur 0 - 475 m (Ref. 6793). Temperate; 61°N - 31°N, 172°W - 116°W
Northeast Pacific: Shumagin Islands in the western Gulf of Alaska to Ensenada, Baja California, Mexico. Possibly occurring in the Bering Sea (Ref. 6793).
Length at first maturity / Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm 70.5, range 61 - 76 cm
Max length : 152 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 2850); poids max. publié: 59.1 kg (Ref. 40637); âge max. reporté: 25 années (Ref. 55701)
Description synthétique
Clés d'identification | Morphologie | Morphométrie
Épines dorsales (Total) : 24 - 27; Rayons mous dorsaux (Total) : 21 - 24; Épines anales: 3; Rayons mous anaux: 21 - 24; Vertèbres: 55 - 59. Anal spines of adults buried in flesh, third spine closely applied to first ray (Ref. 6885). Head without scales; fleshy cirrus above each eye; large mouth; maxilla reaching almost to vertical from posterior margin of eye. Jaws with small pointed teeth interspersed with large fanglike teeth (Ref. 48751).
Ranges from the intertidal to 475 m depth (Ref. 6793). Adults are found near rocks, inshore and to 427 m (Ref. 2850). Young occur on sand or mud bottom of bays and inshore areas (Ref. 2850). Both migratory and non-migratory populations exist (Ref. 6885). Adults feed mostly on other fishes but also take crustaceans, octopi and squid (Ref. 4925). Young feed on copepods and other small crustaceans (Ref. 6885). A very important sport and commercial species (Ref. 2850). The liver is rich in vitamin A (Ref. 6885). Marketed fresh and frozen; eaten steamed, fried, broiled, boiled, microwaved and baked (Ref. 9988). Has sharp teeth and gill rakers that can cut fingers if handled.
Eggs are deposited in crevices or under rocks (Ref. 6885). Male guards the eggs until they hatch.
Eschmeyer, W.N., E.S. Herald and H. Hammann, 1983. A field guide to Pacific coast fishes of North America. Boston (MA, USA): Houghton Mifflin Company. xii+336 p. (Ref. 2850)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Menace pour l'homme
Traumatogenic (Ref. 13513)
Utilisations par l'homme
Pêcheries: commercial; pêche sportive: oui
Outils
Can't connect to MySQL database fbquizv2. Errorcode: Too many connections